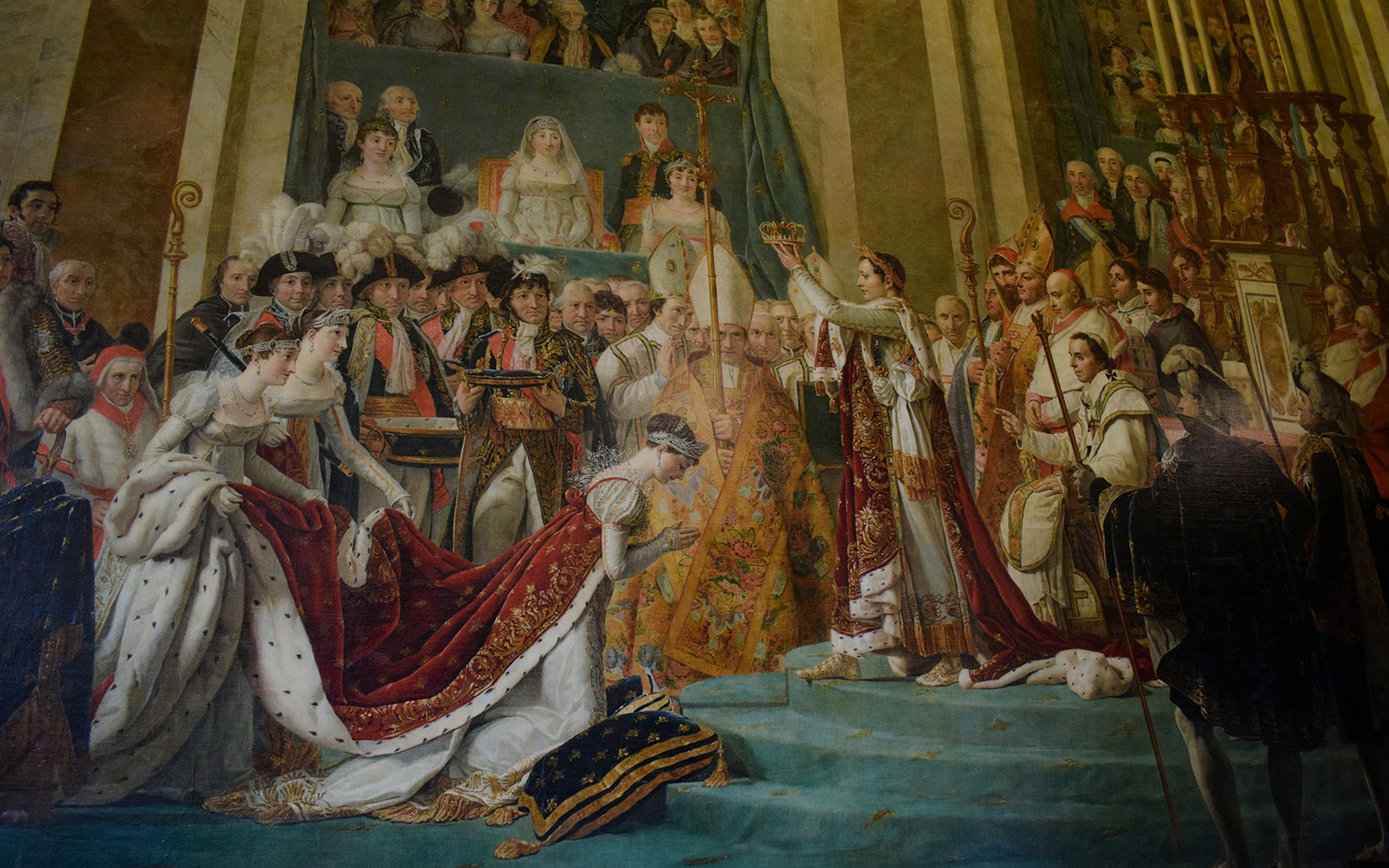
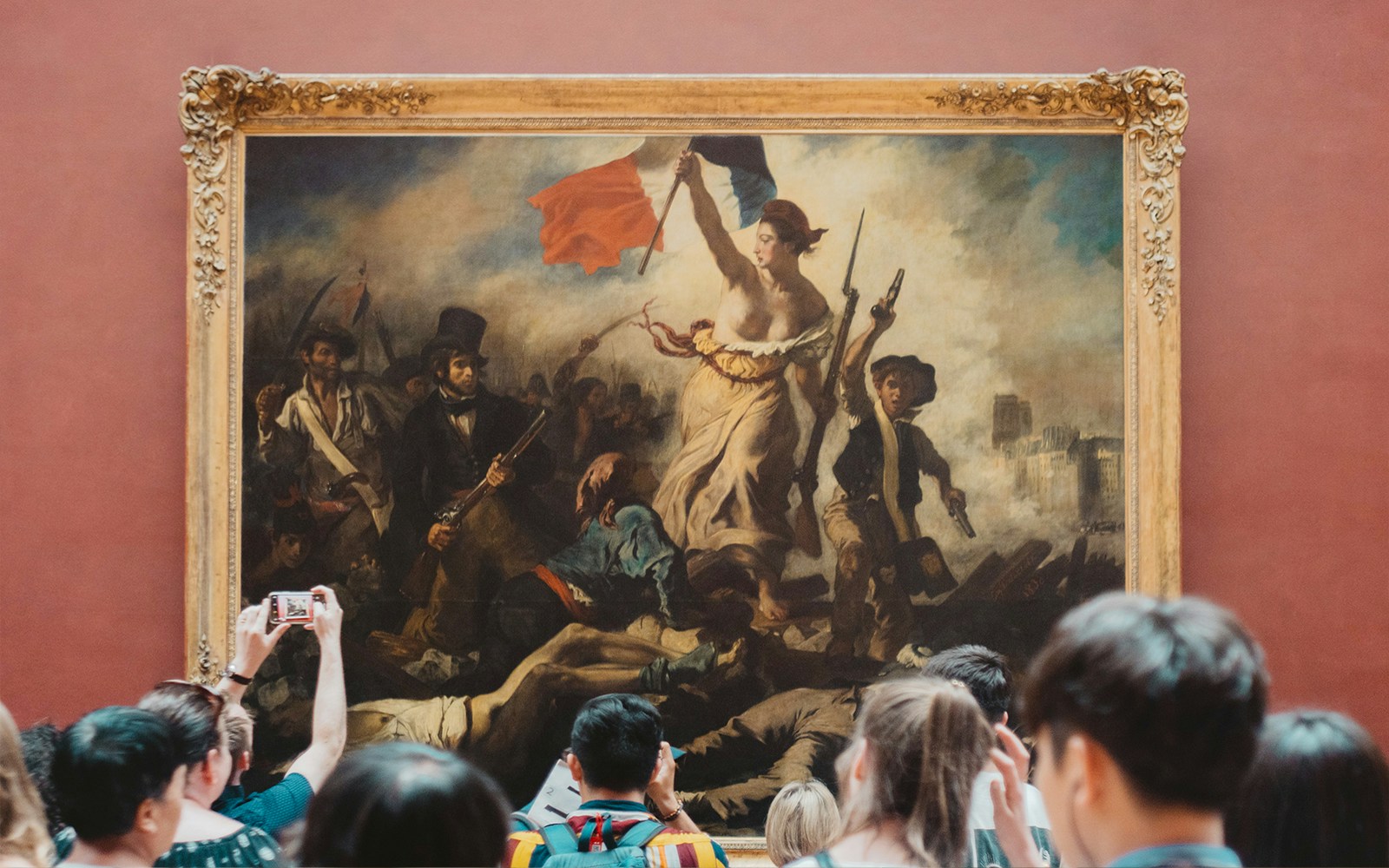- Focus: European paintings from the 13th to the 19th centuries.
- Key Highlights: Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci, The Wedding at Cana by Veronese, Liberty Leading the People by Eugène Delacroix
- Significance: Features works by masters like Raphael, Rembrandt, Vermeer, and Titian.
Dive into the Louvre’s diverse collections
With over 35,000 masterpieces spread across eight departments, the Louvre can feel like a maze. Here's how to navigate its treasures like a pro.
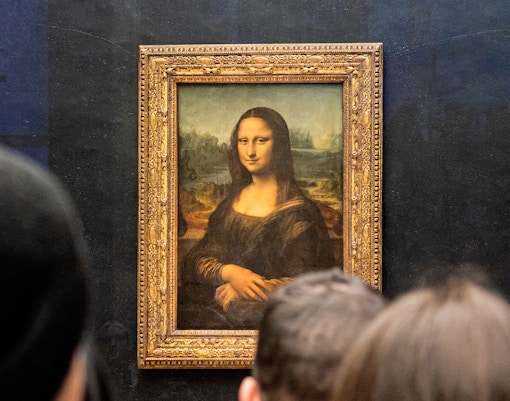

Paintings
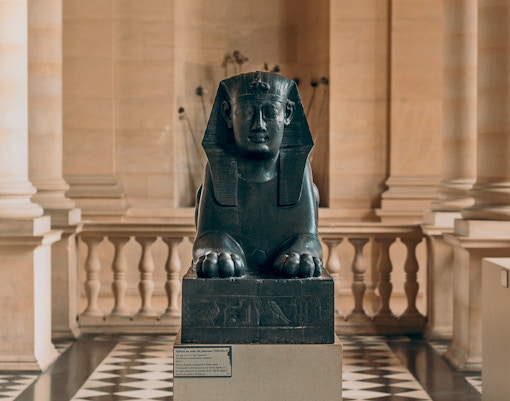

Egyptian Antiquities
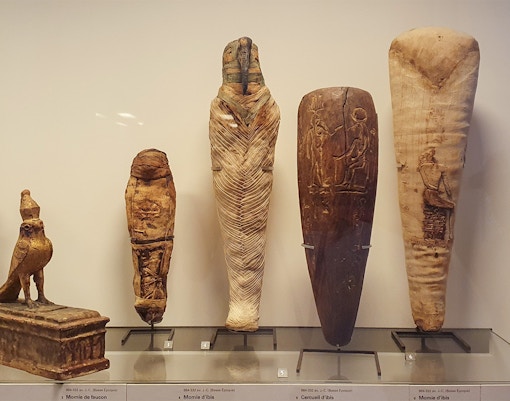
- Focus: Ancient Egyptian culture from prehistory to the Byzantine era.
- Key Highlights: Great Sphinx of Tanis, Sarcophagi, mummies, and daily life artifacts like tools and jewelry.
- Significance: Offers a comprehensive view of pharaonic art, including monumental sculptures and funerary objects.
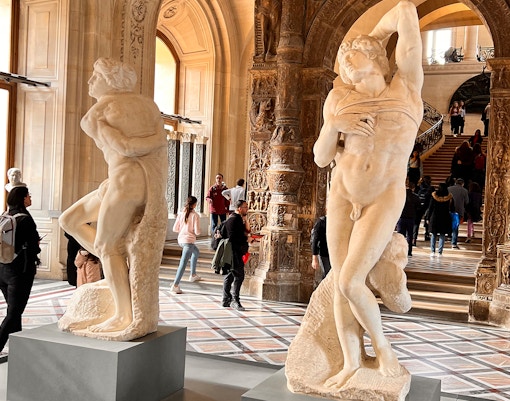

Sculptures
- Focus: Freestanding works from medieval to modern Europe and beyond.
- Key Highlights: Michelangelo’s Dying Slave and Rebellious Slave and The Seated Scribe
- Significance: Celebrates the human form through various periods and styles.

Near Eastern Antiquities
- Focus: Civilizations of Mesopotamia, Persia, and the Levant.
- Key Highlights: Code of Hammurabi, and Winged Human-Headed Bulls (Lamassu) from Khorsabad
- Significance: Explores the cradle of civilization with artifacts from the earliest urban societies.
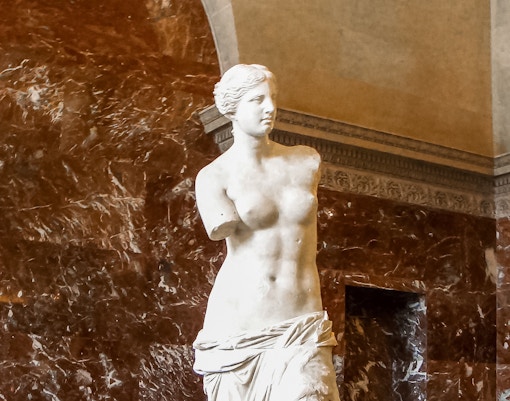

Greek, Etruscan, and Roman Antiquities
- Focus: Classical art and artifacts from the Mediterranean basin.
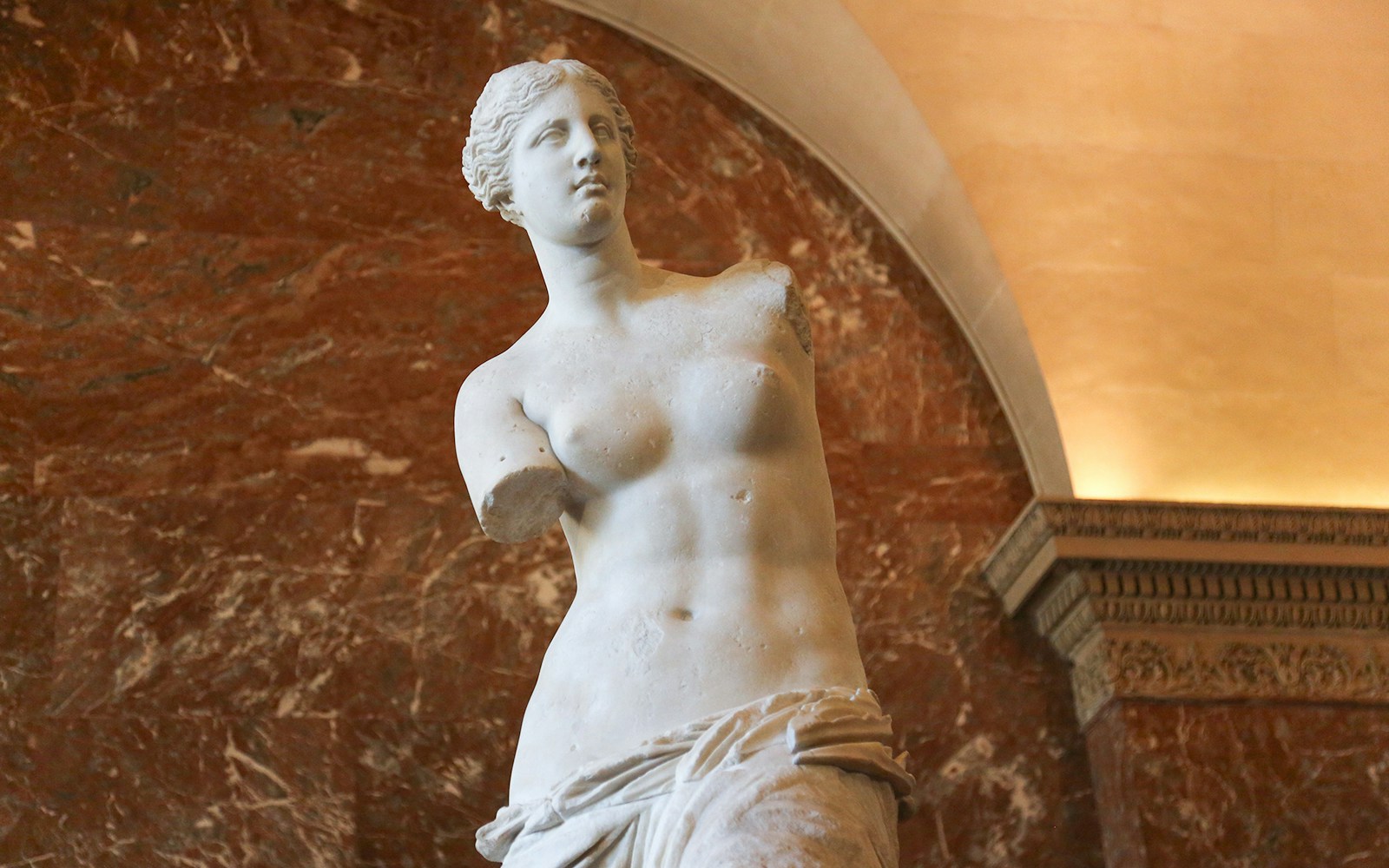
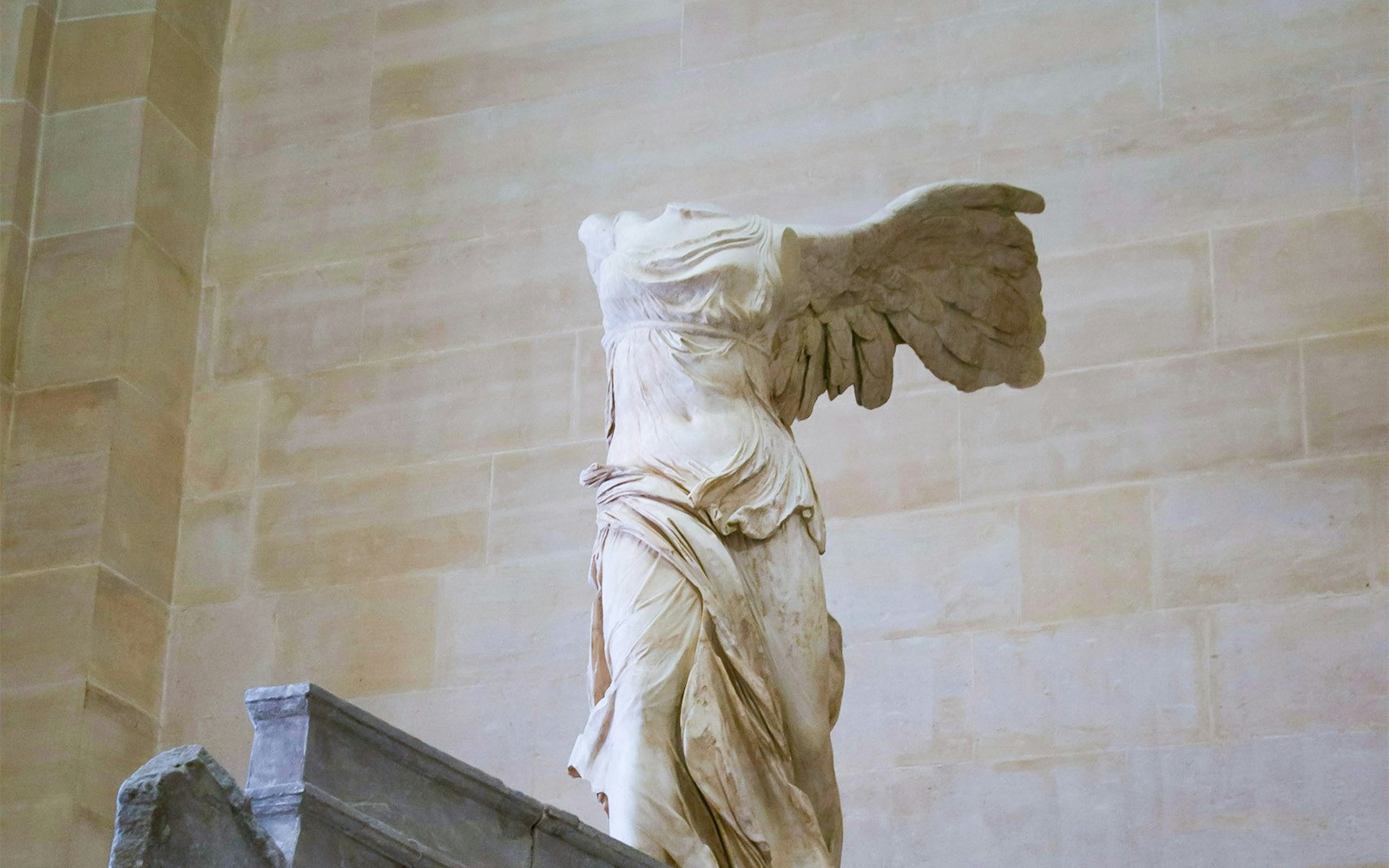
- Key Highlights: Venus de Milo and Winged Victory of Samothrace
- Significance: Showcases the artistic and cultural achievements of the ancient world.
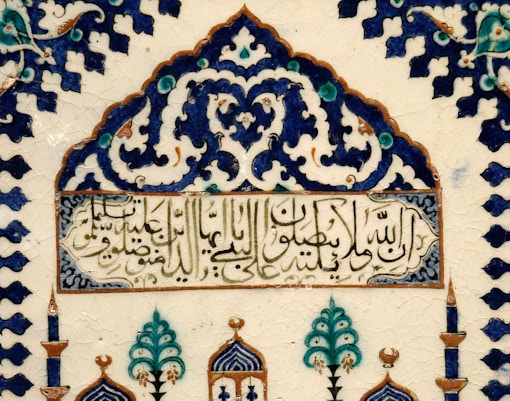

Islamic Art
- Focus: Art from Islamic cultures spanning the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe.
- Key Highlights: Pyxis of al-Mughira, ceramic tiles, textiles, and illuminated manuscripts.
- Significance: Celebrates the beauty and innovation of Islamic artistic traditions.
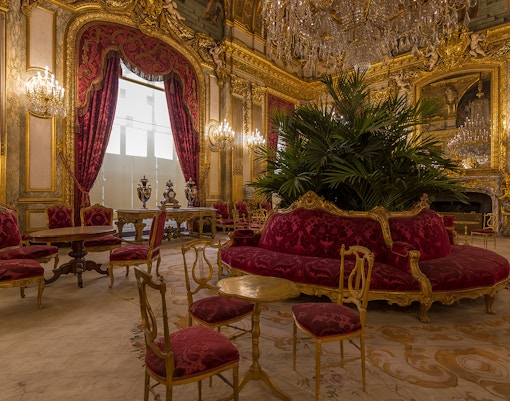

Decorative Arts
- Focus: European decorative pieces from the Middle Ages to the 19th century.
- Key Highlights: Napoleon III’s Apartments, clocks, furniture, and exquisite jewelry.
- Significance: A testament to European craftsmanship and luxury.

Prints and Drawings
- Focus: Works on paper, including drawings, engravings, and illuminated manuscripts.
- Key Highlights: Rare sketches by Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, and Rembrandt.
- Significance: Offers insight into the creative process and evolution of artistic ideas.